Name _____________________ Date _______________ Period __________
Notes 4-9: Isosceles and Equilateral Triangles
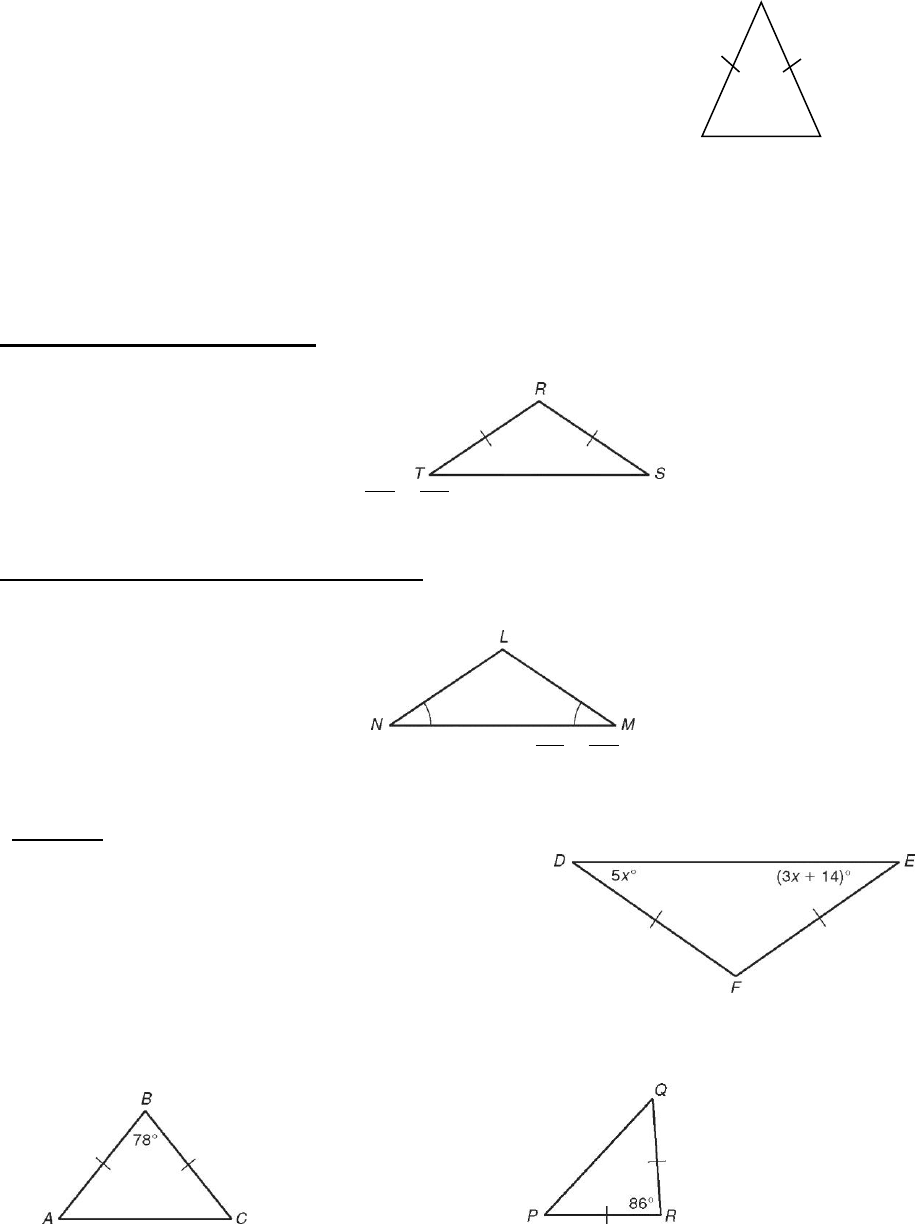
What is an isosceles triangle? ________________________________________________
The congruent sides are called the legs.
The third side is called the base.
The angle opposite the base is called the vertex angle.
The angles opposite the congruent sides are called the base angles.
(These are the angles that are adjacent to the base.)
If a triangle has two congruent sides, does the triangle also have two congruent angles?
Isosceles Triangle Theorem
If ________sides of a triangle are congruent, then the ______________the sides are congruent.
If
,RT RS
then T S.
Converse of Isosceles Triangle Theorem
If __________________of a triangle are congruent, then the ________________those angles are
congruent.
If N M, then
.LN LM
You can use these theorems to find angle measures in isosceles triangles.
Example
Find m∠E in DEF.
m∠D m∠E Isosceles Thm.
5x 3x + 14 Substitute the given values.
Solve for x.
Find m∠E
Find each angle measure.
1. m∠C _____________________ 2. m∠Q _____________________
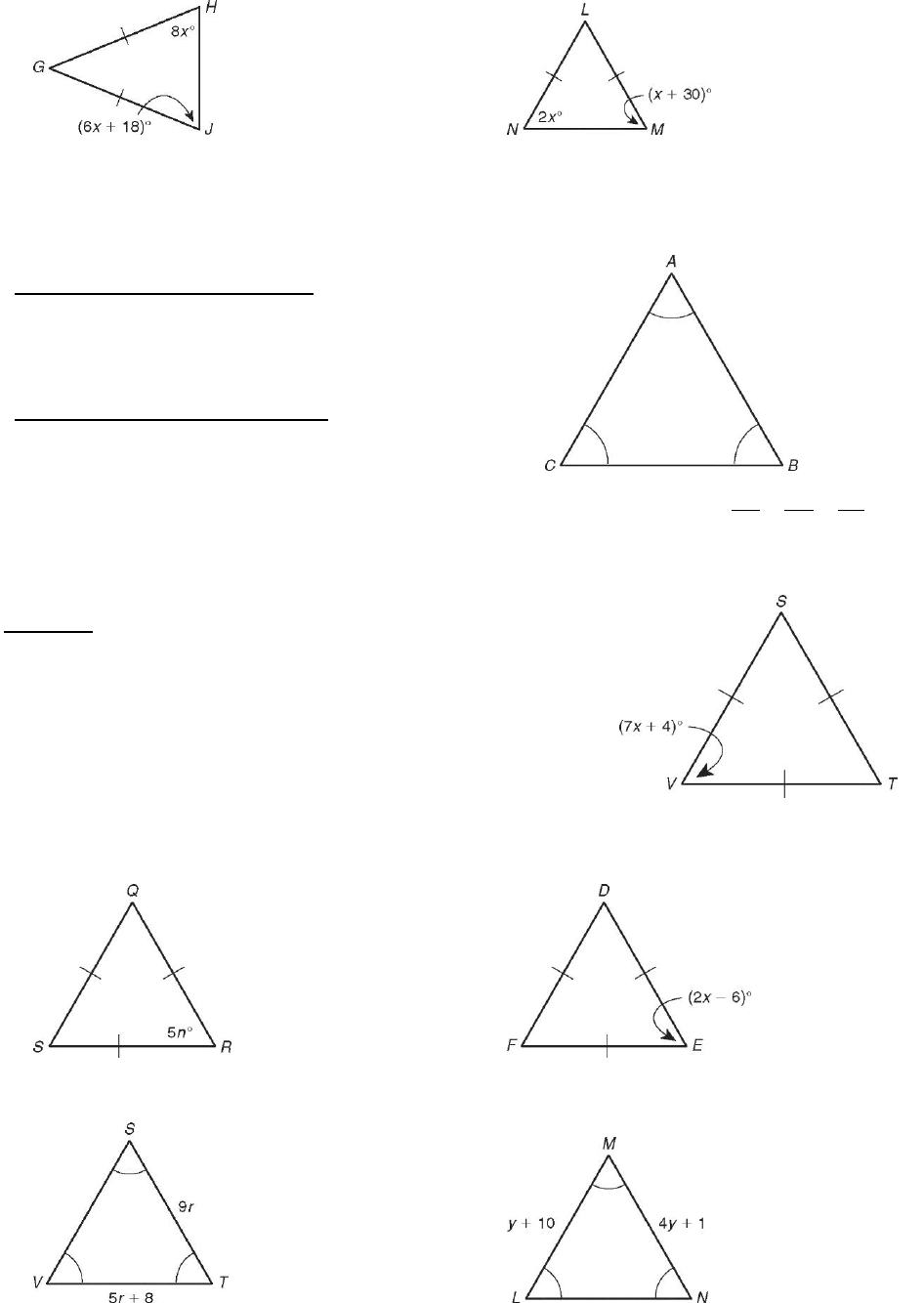
3. m∠H _____________________ 4. m∠M _____________________
You can use these theorems to find values in equilateral triangles.
Example
Find x in STV.
STV is equiangular. Equilateral → equiangular
7x + 4 60 The measure of each ∠ of an
equiangular is 60.
Solve for x.
.
Find each value.
5. n _____________________ 6. x _____________________
7. VT _____________________ 8. MN __________________
Equilateral Triangle Corollary
If a triangle is equilateral, then it is equiangular.
(equilateral equiangular )
Equiangular Triangle Corollary
If a triangle is equiangular, then it is equilateral.
(equiangular equilateral )
If A B C, then
AB BC CA
.
